Most streaming media devices and smart devices connect to the internet by Wi-Fi or by an ethernet connection. For devices you want to connect via ethernet, connect an ethernet cable to the device and plug the other end of the cable to an ethernet jack in your home that is connected to your gateway or your router. For Wi-Fi connections, you will need your Wi-Fi network name (sometimes called an SSID) and its associated password.
Warning: When connecting devices make sure to not connect them both physically via a cable and wirelessly to your router. This can cause serious problems with your connection and service.
Wi-Fi signal may be too weak. Internet signal strength does not necessarily equate to internet speed. Use a speed testing website such as Ookla, Speakeasy or Google.
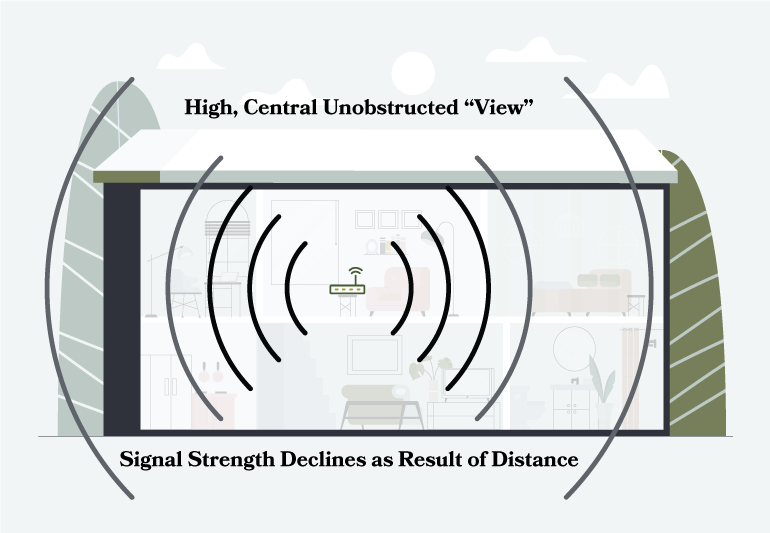
Too many impediments (walls, major appliances, electrical panels, etc.) between the gateway or router and your internet device.
Problem: Even with an optimized gateway or router location, you cannot reach all areas of your home.
Solution: Increase the range your gateway or router, install a more powerful Wi-Fi router, add a range extender, or install a mesh network.
How far Wi-Fi coverage travels will depend on your router's strength, the number of floors or walls signals must pass through, and the size of your home. Check you Wi-Fi device box or product webpage to learn how far your network will go.
You can easily expand your Wi-Fi with wired network extenders or wireless range extenders:
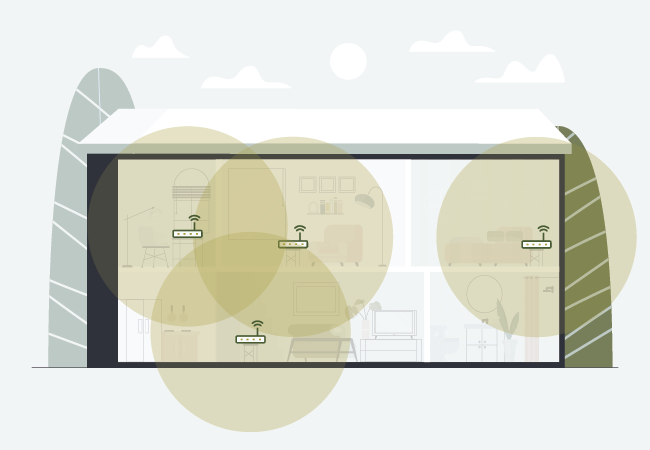
You may already own one or more Wi-Fi Repeaters. Repeaters use older technology that is prone to delays and drop-outs, especially when connecting to multiple devices. If you still have a repeater, upgrade to range extenders or network extenders for better internet performance.